In this Topic Hide
The device statement defines how a device is connected in the circuit, and lists the values for the individual device parameters. If a device requires a device model or some initial condition, such information is also defined in the device statement. The format for a device statement is defined as follows:
| DeviceName NodeName {Values|ModelName} [InitConds] |
| DeviceName | is a legal device name |
| NodeName | is a sequence of legal node names |
| Values | is either a floating-point entry to stand for value or a sequence of parameter assignments |
| ModelName | is the legal name of a compatible model. The symbol {Values|ModelName} means Values and ModelName are mutually exclusive. If a device requires a model name, no Values would be given in the device statement and vice versa |
| InitConds | is a sequence of legal initial condition specifications. The symbol [InitConds] means the presence of the InitConds fields is optional since only some devices require initial conditions. |
Each node in the circuit must be assigned a unique name. A legal node name is either a positive integer or zero. Remember that node 0 is traditionally reserved to represent the ground node. Also note that:
Most of the circuit elements discussed in this chapter are two-terminal elements. For any general two-terminal element, there is a positive node n+ and a negative node n- as shown in the diagram below:
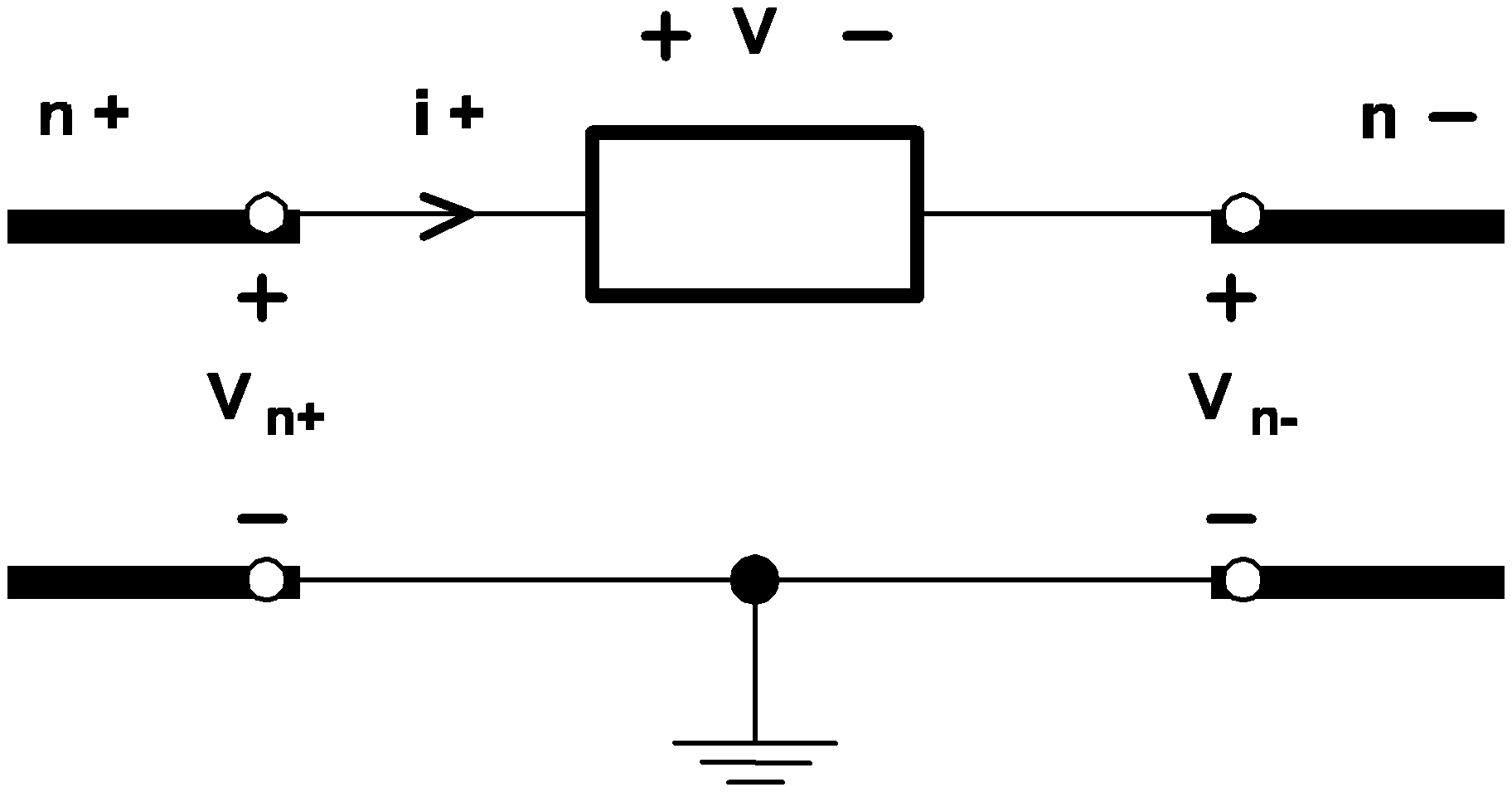
| V = Vn+ - Vn- |
When the current through a two-terminal device is mentioned in this manual, it refers to the current measured in the direction from the positive node through the element to the negative node. Thus, a positive current indicates that there is a net flow of charge into the positive node, through the two-terminal element, and then out of the negative node.
With these sign conventions for voltages and currents, a positive voltage-current product indicates that electric power is instantaneously flowing into the corresponding two-terminal element, whether it is a voltage or current source, a resistor, or any other two-terminal element.
Parameters such as the initial conditions for devices are entered in a format called parameter assignments. The format is
| KEYWORD=value |
| KEYWORD | is the corresponding keyword representing the descriptive name of the parameter, |
| = | is the equal sign ('='), and |
| value | is the value assigned to the parameter. |
The four controlled sources, the simple transistor switch, and the simple switch are each controlled by a controlling variable that is external to the device. There are three types of controlling variables:
|