Sensitivity and Worst-case Analysis
The sensitivity of any measured scalar value to component variation can be found by running a DVM sensitivity analysis. Examples for a sensitivity analysis include peak overshoot/undershoot during a load transient and peak inductor current when in current limit. The sensitivity of scalars such as gain_margin and phase_margin can be found during an AC analysis.
Setting up a sensitivity analysis starts with identifying at least one scalar value you want to examine the sensitivity for. The scalar values can be automatically generated by DVM or created by a post-process script. Starting with version 7.00, the scalars can be generated from fixed-probe measurements which DVM automatically converts to scalar values. Each DVM sensitivity analysis provides a complete report that details the relative and absolute sensitivity of each scalar to the specified component variation.
The DC/DC buck converter example in this topic uses the built-in Bode plot analysis to examine the sensitivity of the following scalar values with variations in power stage and feedback component values:
- gain_margin
- phase_margin
- MAX(VLOAD)
- MIN(VLOAD)
- AVG(VLOAD)
Each scalar value in the above list is automatically generated by DVM and therefore the sensitivity of the scalar can be measured. You can download the DC/DC buck converter example as part of the DVM Tutorial example schematics and supporting files. The converter schematic is located in the LTC3406B directory of the zip archive, and has the filename of LTC3406B Sensitivity.sxsch.
In this topic:
Requirements
DVM sensitivity analysis requires a working DVM schematic design plus the following four text files. Although these files can have any name, in this document we refer to the files with these generic names:
- A sensitivity_base.testplan file that produces at least one scalar value
- A sensitivity_function.def file that defines the target scalar names and corresponding tests that produce those scalars
- A sensitivity_parameter.def file that defines which parameters to vary during the sensitivity analysis
- A sensitivity_tolerance.def file that defines the 3-sigma tolerance for each parameter
Multiple versions of these files can be defined, which files are used is specified on the DVM control symbol:
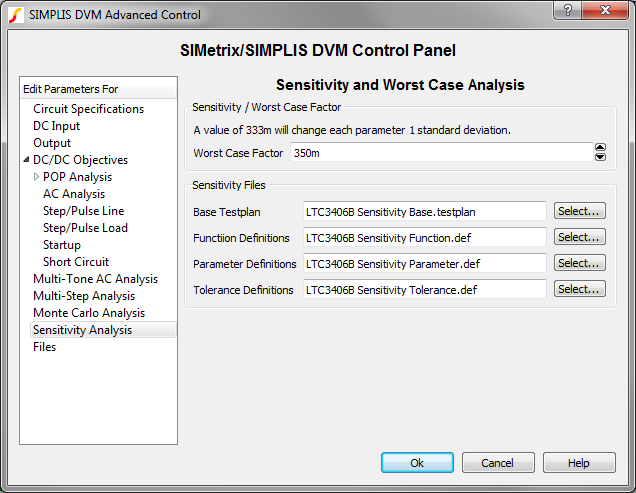
Step 1: Define Scalars and Tests
The sensitivity_function.def text file defines the scalars to be measured and the test(s) to run.
- The first column lists the scalar function(s) to be measured. The scalar name in this column must not contain spaces nor equal signs.
- The second column is the display name for the scalar. This display name also appears in the sensitivity_parameter.def file and is used in the output report. The name in this column can contain spaces and punctuation.
- The third column indicates the test that DVM will execute to find the scalar identified in the first column. The test specified in this column also appears in the sensivity_base.testplan file.
Each scalar is added one per line to the file. DVM automatically figures out how many tests to run in order to find the sensitivity of the scalar functions listed in the file.
The following example includes the file name and the schematic name in comments on the first and second lines.
| *** sensitivity_function.def | ||
| *** SyncBuckSensitivity.sxsch | ||
| *** | ||
| *** FUNC | FUNC DISPLAY NAME | LABEL |
| gain_margin | Gain Margin | Ac Analysis|Bode Plot |
| phase_margin | Phase Margin | Ac Analysis|Bode Plot |
| MAX(VLOAD) | VLOAD Max | Transient|Step Load|50% Load to 100% Load |
| MIN(VLOAD) | VLOAD Min | Transient|Step Load|100% Load to 50% Load |
| AVG(VLOAD) | VLOAD Avg | Steady-State|Steady-State |
Step 2: Setting up the Testplan
DVM needs a sensitivity_base.testplan file to set up the circuit for simulation. Now that you have defined the scalars and tests that you want to use, you can set up the testplan that must include a label column with entries that match exactly the labels in the sensitivity_function.def file.
| *** | ||||
| *** sensitivity_base.testplan | ||||
| *** SyncBuckSensitivity.sxsch | ||||
| *** | ||||
| *?@ Analysis | Objective | Source | Load | Label |
| *** | ||||
| Ac | BodePlot(OUTPUT:1) | Source(INPUT:1, Nominal) | Load(OUTPUT:1, 50%) | Ac Analysis|Bode Plot |
| Transient | StepLoad(OUTPUT:1, 50%, 100%) | Source(INPUT:1, Nominal) | Transient|Step Load|50% Load to 100% Load | |
| Transient | StepLoad(OUTPUT:1, 100%, 50%) | Source(INPUT:1, Nominal) | Transient|Step Load|100% Load to 50% Load | |
| Steady-State | Steady-State | Source(INPUT:1, Nominal) | Load(OUTPUT:1, 50%) | Steady-State|Steady-State |
Step 3: Defining Parameters to Vary
The sensitivity_parameter.def file specifies the parameters to vary during the sensitivity analysis.
- The first column contains the display names exactly as you entered them in the sensitivity_function.def file.
- The remaining columns are a tab-separated list of parameters. Note: In most cases, these parameters are component references; however, DVM can also reach down inside each hierarchical component and change parameters. In the following example, U1.U3.C1, U1.U3.C2, U1.U3.R2 represent hierarchical components, where U1 and U3 are the first two levels, with C1, C2, and R2 as the components to be varied.
| *** sensitivity_parameter.def | |||||||
| *** SyncBuckSensitivity.sxsch | |||||||
| *** | |||||||
| *** FUNC DISPLAY NAME | PARAM1 | [PARAM2..PARAMn] | |||||
| Gain Margin | L1 | C1 | R2 | R3 | |||
| Phase Margin | U1.U3.C1 | U1.U3.C2 | U1.U3.R2 | ||||
| VLOAD Max | L1 | C1 | R2 | R3 | U1.U3.C1 | U1.U3.C2 | U1.U3.R2 |
| VLOAD Min | L1 | C1 | R2 | R3 | U1.U3.C1 | U1.U3.C2 | U1.U3.R2 |
| VLOAD Avg | L1 | R2 | R3 | ||||
Step 4: Defining Component Tolerances
The final step is to define the tolerances of the components in the sensitivity_tolerance.def file. DVM interprets these tolerances as +/- 3 sigma limits.
The sensitivity_tolerance.def file has three mandatory columns and two optional columns.
- The names in the first column must exactly match the display names in the in the sensitivity_function.def and the sensitivity_parameter.def files.
- The second and third columns, NTOL and PTOL, are required and contain the tolerances from nominal. The values can be expressed in % of nominal or in absolute delta from nominal.
- The fourth column, LOT, is optional to declare components which move as a lot.
- The fifth column, MATCH, is to define a matching tolerance.
To make certain that each parameter is assigned a value, you can copy each unique parameter from sensitivity_parameter.def and paste it on its own line in the sensitivity_tolerance.def file, insert a tab and then add the tolerances with tabs between the specifications for each component. The sensitivity_tolerance.def file for this example looks like the following:
| *** sensitivity_tolerance.def | ||||
| *** SyncBuckSensitivity.sxsch | ||||
| *** | ||||
| *** PARAMETER | NTOL | PTOL | LOT | MATCH |
| L1 | 10% | |||
| C1 | 20% | |||
| R2 | 5% | 5% | feedback_resistors | 1% |
| R3 | 5% | 5% | feedback_resistors | 1% |
| U1.U3.R2 | 20% | |||
| U1.U3.C1 | 20% | |||
| U1.U3.C2 | 20% | |||
| V2.DC_VOLTAGE | .5 | .5 | ||
| I1.LOAD_RESISTANCE | 1.003340 | 28 | ||
Running the Sensitivity Analysis Simulation
During a DVM sensitivity analysis, DVM executes a simulation for each component listed in the sensitivity_parameter.def file, adjusting each parameter by the worst-case factor entered in the DVM Control Dialog. For example:
- If you set the worst-case factor to 0.333, DVM adjusts each component value one standard deviation positive.
- If you set the worst-case factor to -0.333 WC, DVM adjusts each component value one standard deviation in the negative direction.
To execute the DVM sensitivity analysis, select from the schematic menu.
The DVM sensitivity analysis for the circuit in this example executes 28 tests, one for the nominal values and one for each parameter. After the sensitivity analysis is complete, an HTML report appears in your browser, detailing the sensitivity of the circuit based on the sensitivity setup files. In addition to the report, the command shell shows the 28 runs which were executed.| Preparing simulation run... |
| Test 1 of 28: Ac Analysis|Bode Plot |
| Test 2 of 28: Ac Analysis|Bode Plot|sensitivity|C1 |
| Test 3 of 28: Ac Analysis|Bode Plot|sensitivity|L1 |
| Test 4 of 28: Ac Analysis|Bode Plot|sensitivity|R2 |
| Test 5 of 28: Ac Analysis|Bode Plot|sensitivity|R3 |
| Test 6 of 28: Ac Analysis|Bode Plot|sensitivity|U1.U3.C1 |
| Test 7 of 28: Ac Analysis|Bode Plot|sensitivity|U1.U3.C2 |
| Test 8 of 28: Ac Analysis|Bode Plot|sensitivity|U1.U3.R2 |
| Test 9 of 28: Steady-State|Steady-State |
| Test 10 of 28: Steady-State|Steady-State|sensitivity|L1 |
| Test 11 of 28: Steady-State|Steady-State|sensitivity|R2 |
| Test 12 of 28: Steady-State|Steady-State|sensitivity|R3 |
| Test 13 of 28: Transient|Step Load|100% Load to 50% Load |
| Test 14 of 28: Transient|Step Load|100% Load to 50% Load|sensitivity|C1 |
| Test 15 of 28: Transient|Step Load|100% Load to 50% Load|sensitivity|L1 |
| Test 16 of 28: Transient|Step Load|100% Load to 50% Load|sensitivity|R2 |
| Test 17 of 28: Transient|Step Load|100% Load to 50% Load|sensitivity|R3 |
| Test 18 of 28: Transient|Step Load|100% Load to 50% Load|sensitivity|U1.U3.C1 |
| Test 19 of 28: Transient|Step Load|100% Load to 50% Load|sensitivity|U1.U3.C2 |
| Test 20 of 28: Transient|Step Load|100% Load to 50% Load|sensitivity|U1.U3.R2 |
| Test 21 of 28: Transient|Step Load|50% Load to 100% Load |
| Test 22 of 28: Transient|Step Load|50% Load to 100% Load|sensitivity|C1 |
| Test 23 of 28: Transient|Step Load|50% Load to 100% Load|sensitivity|L1 |
| Test 24 of 28: Transient|Step Load|50% Load to 100% Load|sensitivity|R2 |
| Test 25 of 28: Transient|Step Load|50% Load to 100% Load|sensitivity|R3 |
| Test 26 of 28: Transient|Step Load|50% Load to 100% Load|sensitivity|U1.U3.C1 |
| Test 27 of 28: Transient|Step Load|50% Load to 100% Load|sensitivity|U1.U3.C2 |
| Test 28 of 28: Transient|Step Load|50% Load to 100% Load|sensitivity|U1.U3.R2 |
Worst-Case Analysis
Before you can run a DVM worst-case analysis, you must first run a DVM sensitivity analysis. When the sensitivity analysis completes, two files are automatically created to be used by the worst-case analysis:
- worstcase_sign.def
- worstcase_lot_sign.def
During the worst-case analysis, each component is set to its worst-case value, which is either PTOL or NTOL based on the sign information in these two files. This means that for a DVM worst-case analysis, each component is set to its worst-case 3 sigma value, and the target scalars from the sensitivity_function.def file are measured.
The worstcase_sign.def for this example contains the following sign information:
| *** worstcase_sign.def | ||
| *** | ||
| *** PARAMETER | FUNC DISPLAY NAME | SIGN |
| L1.L | Gain Margin | - |
| C1 | Gain Margin | + |
| R2 | Gain Margin | + |
| R3 | Gain Margin | + |
| U1.U3.C1 | Phase Margin | + |
| U1.U3.C2 | Phase Margin | - |
| U1.U3.R2 | Phase Margin | + |
| L1 | VLOAD Max | + |
| C1 | VLOAD Max | - |
| R2 | VLOAD Max | + |
| R3 | VLOAD Max | - |
| U1.U3.C1 | VLOAD Max | + |
| U1.U3.C2 | VLOAD Max | + |
| U1.U3.R2 | VLOAD Max | - |
| L1 | VLOAD Min | + |
| C1 | VLOAD Min | - |
| R2 | VLOAD Min | + |
| R3 | VLOAD Min | - |
| U1.U3.C1 | VLOAD Min | + |
| U1.U3.C2 | VLOAD Min | - |
| U1.U3.R2 | VLOAD Min | + |
| L1 | VLOAD Avg | + |
| R2 | VLOAD Avg | + |
| R3 | VLOAD Avg | - |
If this example had not contained components that were LOT matched, the worstcase_lot_sign.def would be an empty file. Since both LOT and MATCH were specified in the sensitivity_tolerance.def file, the worstcase_lot_sign.def file would contain the sign information for those parameters as shown below.
| *** worstcase_lot_sign.def | ||
| *** | ||
| *** LOT | FUNC DISPLAY NAME | SIGN |
| feedback_resistors | Gain Margin | + |
| feedback_resistors | VLOAD Max | + |
| feedback_resistors | VLOAD Min | + |
| feedback_resistors | VLOAD Avg | + |